Goodbye to the traditional Chipotle breaks the mold with this surprising decision to change its menu after years of no change
Say goodbye to boring colors your house will be able to change color automatically thanks to this revolutionary technology
Costco and Real ID have these differences in documentation even the TSA had to clarify for flights
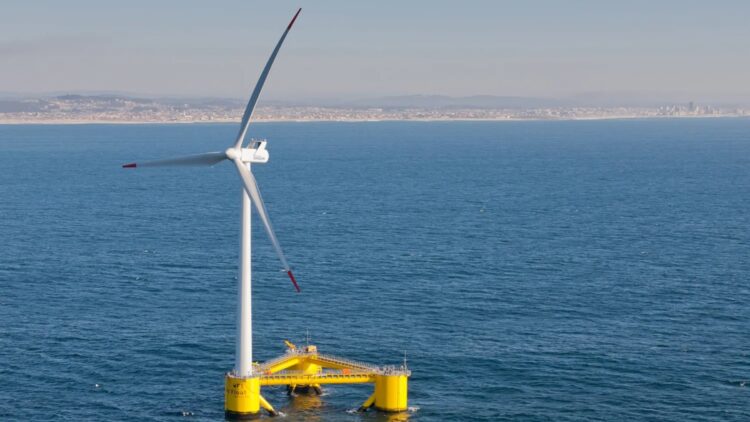
There will soon be a new wind turbine to enhance offshore wind power, a renewable energy source!Wind energy is becoming more and more popular, and there are other clean ways to generate electricity. Wind turbines are used in this wind energy, but a Norwegian business has unveiled a novel floating wind turbine that has the potential to completely transform the clean energy industry. This technical advancement seeks to lower costs and lessen environmental effect while increasing the efficiency of electricity production. A more precise and accessible development of renewable energy is made possible by this revolutionary floating wind turbine.
In most regions of the world, renewable energy sources are growing in popularity, which is beneficial for halting environmental degradation. Let’s examine the operation of these floating wind turbines.
Wind energy
As time goes on, more nations are implementing and looking for environmentally friendly energy production methods. One of these is wind power, which generates electricity when the wind drives the wind turbine’s massive blades. These turbines, which resemble enormous fans with enormous blades, are found in high locations with strong winds.
Even though we already have a large number of these wind turbines, they have certain drawbacks. For example, some of them are quite costly, others are difficult to maintain, and the majority of them don’t function as well if the wind doesn’t blow in a certain direction.
New floating wind turbine
Given all of the issues with the original wind turbines, a Norwegian business has developed a floating wind turbine as a solution. What is this? In terms of design, this new turbine is somewhat similar to the wind turbines we are accustomed to, yet they differ greatly in other ways:
- It can be located in the sea with no need to be attached to the seabed, something impossible with the regular wind turbines. The floating wind turbines float on the sea, as it s mentioned on its name, with the capacity to be located offshore, where the wind is much stronger.
- The new floating turbines have an axis where the blades move and it s like a tube from up to down, whereas the regular turbines go from side to side.
- The new turbines have two parts that move in opposite directions. Imagine two propellers, one on top of the other and moving in different ways.
- Due to all these features, the floating wind turbine can move faster and produce more energy. It s remarkable that it also works even though the wind doesn t come in the perfect direction. What s more, they take less space, but it doesn t affect the electricity production because it produces even more!
How much energy?
30 kW of electricity may be produced by the Norwegian company’s turbines during their initial testing. The Norwegian corporation, however, wants it to be more than 4,265 feet high (higher than many buildings) and reach 40 megawatts (MW).
This would lower the cost of using wind to generate electricity, so more individuals and nations would purchase the product at a lower price. Are there any favorable ramifications for our planet’s future? Yes! Polluting fuels will become obsolete as the number of floating wind turbines increases, and the environment won’t be harmed.
Significance of this invention
These floating wind turbines will benefit from the wind that comes from this location because they may be placed offshore. Additionally, the production is inexpensive, and more electricity will be generated without endangering the environment.
The ideal use of technological advancements is to improve the planet. The possibility of irreversible environmental harm would be far from actual if other businesses continued to create technologies similar to that of Norway.